A power cable is an electrical cable, an assembly of one or more electrical conductors, usually held together with an overall sheath. The assembly is used for transmission of electrical power. Power cables may be installed as permanent wiring within buildings, buried in the ground, run overhead, or exposed. The cables usually consist of conductors, insulations and jacket. The conductor of aluminum ,copper, aluminum-alloy are in common.
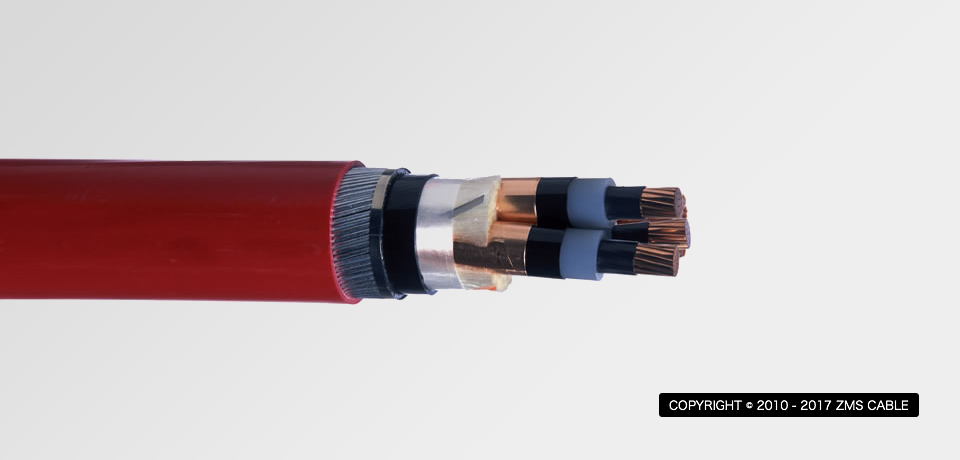

However, with the development of technology and economy, altern-atives type of cables exist: Copper-clad aluminum wire, commonly abbreviated as CCAW or CCA, is an electrical conductor composed of an inner aluminum core and outer copper cladding.
The primary applications of this conductor revolve around weight reduction requirements. These applications include high-quality coils, such as the voice coils in headphones or portable loudspeakers; high frequency coaxial applications, such as RF antennas and cable televisiondistribution cables; and power cables.
CCA was also used in electrical wiring for buildings. The copper/aluminum construction was adopted to avoid some of the problems with aluminum wire, yet retain some of the cost advantage. In the US, solid copper is most commonly used in internal residential 120 V or 240 V wiring.
CCA is also seen in unshielded twisted pair networking cables. These cables are often less expensive than their full-copper counterparts. Experts advise against the use of CCA cables in networks because it is far less reliable and can affect transmission speeds. This is due to a number of factors, important ones being aluminum's much higher electrical impedance compared to copper, and the fact that aluminum is less flexible and tends to break more easily.
The properties of copper-clad aluminum wire include: Higher electrical conductivity than pure aluminum ; Higher strength than aluminum , Electrical connections are typically more reliable than pure aluminum; Less expensive than a pure copper wire; Lighter than pure copper
The skin effect causes alternating current to concentrate on the more-conductive copper cladding of the conductor, causing the resistance of the wire to approach that of a pure copper wire at high frequencies, which makes the copper-clad aluminum wire a good fit for such applications. The skin effect is also utilized in copper-clad steel wire such as RG-6 coax, which is also commonly used in high frequency applications with high strength requirements.
However, it exists two sides for the conductor. The disadvantages of the conductor: Aluminum has a higher resistivity than copper so to achieve the same performance; you need thicker conductors and larger cables.
But purveyors of CCA cables make them the same size as copper ones, increasing the risks. When used for Power over Ethernet, a typical temperature increase in a cable bundle will be around 10?C above ambient, with aluminum conductors that will double or even triple, making cables run hotter and presenting a risk to the current and future network owners.
For the two aspects, we should dialectically research this issue, according to the cable usage of environment and requirements.