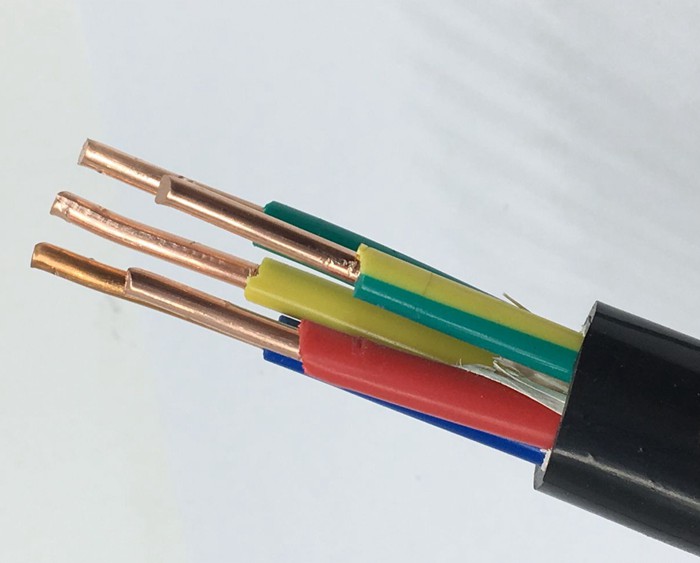
Halogen Free Flame Retardant Cables are a special cable more common and troublesome quality problem is the environmental stress cracking of insulating materials.
Low smoke and halogen-free are abbreviated as LSZH, LSOH, LS0H, LSFH, and OHLS, which is the material classification of wire sheathing in the wire and cable industry.
Low smoke zero halogen wire sheathing is composed of thermoplastic or thermosetting materials that have low smoke emissions when exposed to heat and do not contain halogens themselves.
It also reduces the amount of toxic, corrosive gases produced when it burns.
Low smoke and halogen-free materials are often used in poorly ventilated environments such as airplanes, train cars, or ships.
It is also commonly used in the railroad industry, where there are high-voltage lines or signal lines that transmit the location of trains underneath the railroad.
The use of halogen-free cable materials also reduces the accumulation of toxic gases when the line is damaged by fire or a short circuit.
Halogen-free low-smoke flame retardant cable materials are caused by environmental stress cracking the main reasons are:
Due to the high filling of flame retardant filler such as aluminum hydroxide, magnesium hydroxide causes the strength of the polymer body to reduce, elongation and flexibility also reduce, tear-resistance and cracking resistance inherent.
Halogen-free carriers are generally used low-density polyethylene and EVA, the flame retardant with the mixture of high hardness, in particular, to meet the IEC332-1 flame retardancy (single combustion level, the material.
The corresponding oxygen index is generally greater than and the material hardness at this time is often greater than the shore A90 above.
Based on the metal hydrate as a flame retardant halogen free cable material, high filling properties.
Such as the extrusion process temperature, and the screw compression ratio used improperly, will cause hydrous oxide decomposition and high Cut the polymer off.
As the compression ratio, the extruder speed can not reach the normal level, resulting in the material in the barrel and screw residence time being too long, the friction generated by the high temperature, and the hydrous oxide premature decomposition of the material inside the bubble (Micro hole).
So that the finished product after extrusion mechanical strength and anti-winding ability greatly reduced.
Sudden cooling also adds unfavorable factors.
Polyethylene-based halogen-free low-smoke materials are generally more temperature-sensitive.
Under the conditions of large temperature changes, the internal stress due to thermal expansion and contraction tends to cause cracking in the interface area.
For example, in the north, when a finished cable reel of halogen-free flame retardant cable is placed on the customer's site without packaging, a week later, almost all the cables on the reel were found to have longitudinal cracks on the sunny side of the cable, 1/2 circumference of the disk.
This analysis is due to the cable tray on one side of the sun, one side of the shade, and both sides of the larger temperature difference under the effect of bending stress and material cracking.
Extrusion dies structure type, stretch ratio, and the balance of tension and extrusion stress after the elimination of internal stress have a crucial role.
Generally, use less pressure semi-extrusion mold.
The draw ratio and stretch balance ratio of the inner and outer molds should be controlled at 1: 2 and close to 1 respectively.
The tensile balance rate is calculated as follows:
Where: Dd - Die diameter (mm)
DT - outside diameter of the core (mm)
DCW-- cable insulation or jacket diameter after extrusion (mm)
DBW - core diameter (mm)