
Power cables are cables used to transmit and distribute electrical energy. Power cables are commonly used in urban underground power grids, power station outlet lines, internal power supply for industrial and mining enterprises, and power lines under river water.
In power lines, the proportion of cables is gradually increasing. Power cables are cable products used to transmit and distribute high-power electrical energy in the backbone of power systems, including various voltage levels from 1-500KV and above, and various insulated power cables.
According to the voltage class, it can be divided into medium and low voltage power cables (35 kV and below), high voltage cables (110 kV or more), ultra high voltage cables (275 to 800 kV) and UHV cables (1000 kV and above). In addition, it can be divided into AC cable and DC cable according to current.
Oil-impregnated paper insulated power cable with oil-impregnated paper as insulation power cable. Its application history is the longest. It is safe and reliable, has a long service life and is inexpensive. The main disadvantage is that the laying is limited by the drop. Since the development of non-drip paper impregnation insulation, the problem of drop limitation has been solved, and oil-impregnated paper insulated cables have continued to be widely used.
Plastic insulated power cable The insulation layer is a power cable for extruding plastic. Commonly used plastics are polyvinyl chloride, polyethylene, and crosslinked polyethylene.
The plastic cable has a simple structure, convenient manufacturing and processing, light weight, convenient laying and installation, and is not limited by the installation drop.
Therefore, it is widely used as a medium and low voltage cable, and has a tendency to replace the viscous oil-impregnated paper cable. The biggest drawback is the presence of dendrite breakdown, which limits its use at higher voltages.
Plastic insulated The insulation layer is made of rubber and various compounding agents. After thorough mixing, it is extruded on the conductive core and heated and vulcanized. It is soft and flexible, suitable for occasions with frequent movement and small bending radius.
Commonly used as insulating rubber compound is natural rubber-styrene-butadiene rubber mixture, ethylene-propylene rubber, butyl rubber and the like.
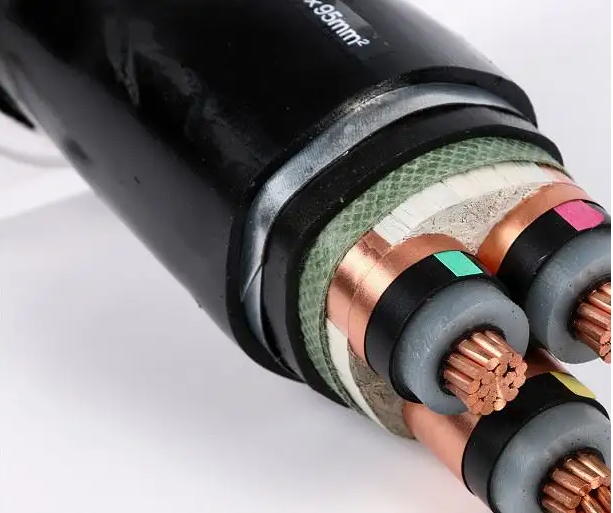
Low-voltage cable: It is suitable for fixed power transmission on the transmission and distribution lines with AC 50Hz and rated voltage of 3kv and below.
Medium and low voltage cable: (generally refers to 35KV and below): PVC insulated cable, polyethylene insulated cable, XLPE insulated cable.
High-voltage cable: (generally 110KV and above): polyethylene cable and XLPE insulated cable.
Ultra high voltage cable: (275 ~ 800 kV).
UHV cable: (1000 kV and above).
The basic structure of the power cable consists of a core (conductor), an insulating layer, a shielding layer and a protective layer.
The core is the conductive part of the power cable that is used to carry electrical energy and is the main part of the power cable.
The insulating layer electrically isolates the core from the earth and the cores of different phases to ensure electrical energy transmission, and is an indispensable component of the power cable structure.
Power cables of 15KV and above generally have a conductor shield and an insulating shield.
The role of the protective layer is to protect the power cable from external impurities and moisture, and to prevent external forces from directly damaging the power cable.