In electricity transmission, underground high voltage cables have emerged as a vital component of modern electrical infrastructure.
These cables serve as a conduit for transmitting high voltage electricity beneath the earth's surface, offering numerous advantages over traditional overhead transmission lines.
This essay delves into underground high voltage cables' classification, applications, and benefits, shedding light on their pivotal role in ensuring reliable and efficient power distribution.
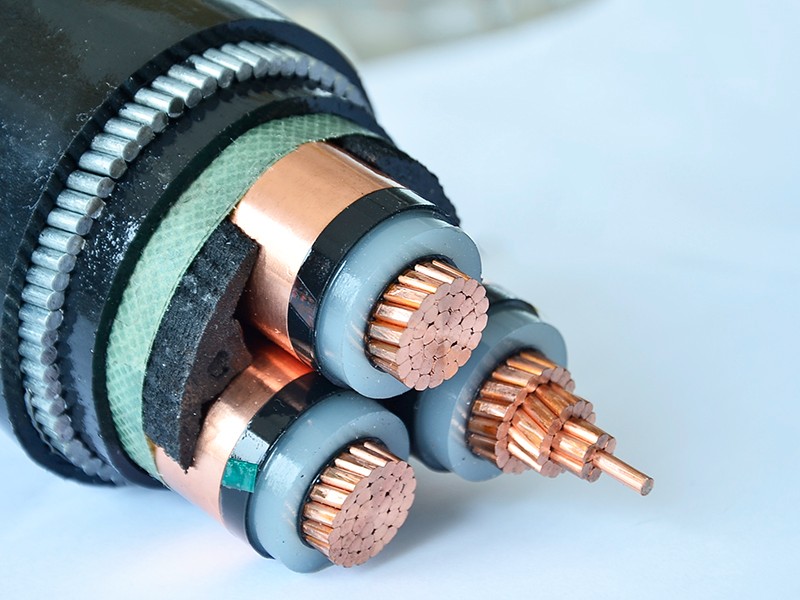
Underground high voltage cables can be categorized based on various criteria, including insulation type, voltage level, and construction design.
Here are some common classifications:
Oil-Filled Cables: These cables feature paper-insulated conductors immersed in oil, providing efficient cooling and insulation.
Gas-Insulated Cables: Gas-insulated cables utilize pressurized sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) or nitrogen gas to insulate the conductors, offering compactness and high reliability.
Extruded Cables: Extruded cables employ synthetic polymers such as cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) or ethylene propylene rubber (EPR) for insulation, ensuring excellent electrical properties and durability.
Medium Voltage (MV) Cables: Typically used for voltages ranging from 1 kV to 36 kV, MV cables are suitable for urban distribution networks and industrial applications.
High Voltage (HV) Cables: HV cables are designed for voltages exceeding 36 kV, catering to long-distance transmission and interconnection of power grids.
Single-core cables: Single-core cables consist of a single conductor surrounded by insulation and metallic sheath, suitable for high voltage transmission.
Three-core cables: Three-core cables feature three insulated conductors bundled together within a common sheath, offering balanced currents and minimizing electromagnetic interference.
Underground high voltage cables find a wide array of applications across various sectors due to their versatility and reliability. Some prominent applications include:

Underground high voltage cables play a crucial role in urban power distribution networks, delivering electricity to residential, commercial, and industrial areas without the visual intrusion associated with overhead lines.
These cables are often preferred in densely populated urban areas where space constraints or aesthetic considerations limit the installation of overhead transmission lines.
Submarine high voltage cables facilitate the transmission of electricity across water bodies, connecting islands, offshore installations, and mainland grids.
They are utilized in offshore wind farms, interconnecting underwater power grids, and supplying electricity to remote coastal regions, offering a reliable and efficient solution for offshore energy transmission.
Industries with critical power requirements, such as manufacturing plants, data centers, and petrochemical facilities, rely on underground high voltage cables for uninterrupted power supply.
These cables are preferred for their ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions, electromagnetic interference, and mechanical stress, ensuring reliable operation in industrial environments.
Underground high voltage cables play a vital role in integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, into the grid.
They enable the transmission of electricity from remote renewable energy installations to urban centers, overcoming geographical barriers and reducing transmission losses.
In railway electrification projects, underground high voltage cables are utilized to power trains, signaling systems, and railway infrastructure.
These cables offer enhanced safety by eliminating the risk of contact with overhead lines, especially in densely populated areas and tunnels.
Underground high voltage cables facilitate cross-border interconnections between neighboring countries, enabling the exchange of electricity and enhancing grid stability.
They contribute to the establishment of regional energy markets, promoting energy security, and facilitating the integration of renewable energy resources.
Underground high voltage cables offer several advantages compared to overhead transmission lines, making them an attractive choice for various applications:
Underground cables eliminate the visual impact associated with overhead lines, preserving the natural landscape and enhancing the aesthetic appeal of urban and rural areas.
They are particularly suitable for heritage sites, scenic locations, and environmentally sensitive areas where preserving visual aesthetics is paramount.
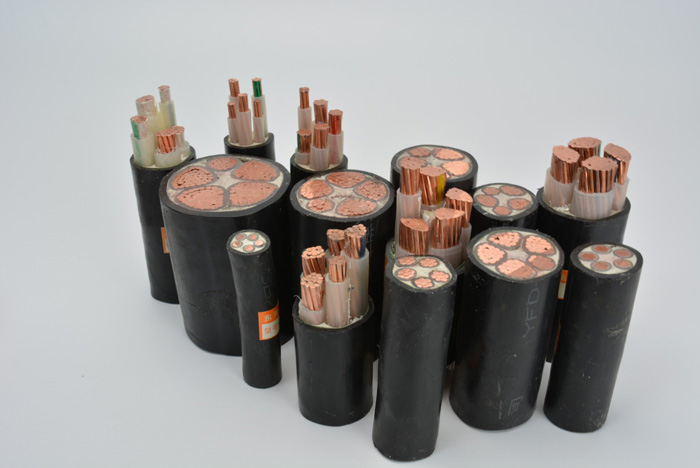

Underground cables are less susceptible to weather-related disruptions, such as lightning, high winds, and ice accumulation, which often affect overhead lines.
They offer higher reliability and lower outage rates, contributing to uninterrupted power supply and minimizing downtime for end-users.
Underground high voltage cables minimize environmental disturbance by eliminating the need for clearing vegetation, reducing habitat fragmentation, and preserving biodiversity.
They mitigate the risk of wildlife-related outages and minimize the visual and noise pollution associated with overhead transmission lines.
Underground cables pose lower risks of accidental contact, electrocution, and wildfires compared to overhead lines, enhancing public safety and reducing liability concerns.
They are less susceptible to vandalism, theft, and damage from external factors, contributing to a safer operating environment.
Underground cables require less space compared to overhead lines, making them suitable for urban areas, narrow rights-of-way, and congested corridors.
They offer flexibility in routing and installation, efficiently utilizing limited land resources and minimizing land acquisition costs.
Underground high voltage cables exhibit greater durability and longevity due to protection from environmental factors such as UV radiation, extreme temperatures, and atmospheric pollution.
They have a longer service life expectancy compared to overhead lines, resulting in lower lifecycle costs and higher overall reliability.
Underground high voltage cables represent a cornerstone of modern electrical infrastructure, offering a reliable, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing solution for power transmission and distribution.
With diverse applications spanning urban distribution networks, renewable energy integration, industrial facilities, and cross-border interconnections, these cables play a pivotal role in ensuring energy security, environmental sustainability, and grid reliability.
As technology continues to advance, underground high voltage cables are poised to play an increasingly significant role in shaping the future of electricity transmission, ushering in an era of cleaner, smarter, and more resilient energy systems.