In the realm of electrical installations, safety is paramount. One crucial aspect of ensuring safety is the use of flame retardant cables. These cables are designed to resist the propagation of fire, limiting its spread and minimizing damage to property and personnel. In this article, we will delve into the world of flame retardant cables, exploring their types, classification, and applications across various industries.
Flame retardant cables are specially engineered to inhibit the spread of fire along their length. They are constructed using materials that possess inherent fire-resistant properties or are treated with flame-retardant additives. These cables are designed to withstand high temperatures and resist combustion, thereby reducing the risk of fire-related accidents in electrical installations.
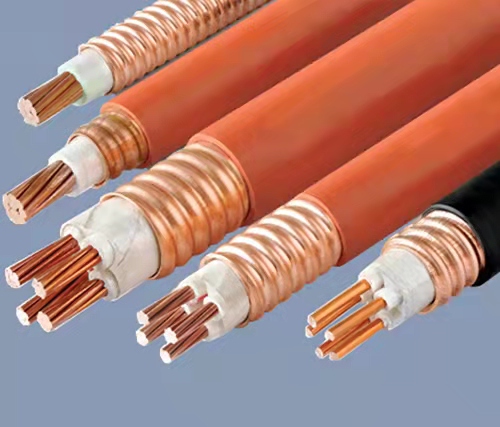

Flame retardant cables come in various types, each tailored to specific applications and environmental conditions. Some common types of flame retardant cables include:
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) insulated flame retardant cables are among the most widely used variants. These cables feature PVC insulation treated with flame-retardant additives, such as antimony trioxide or aluminum hydroxide, to enhance their fire resistance. PVC insulated flame retardant cables are commonly used in indoor electrical wiring, power distribution systems, and building infrastructure.
LSZH cables are designed to minimize the emission of smoke and toxic gases in the event of a fire. Unlike conventional cables that release harmful halogen gases when exposed to high temperatures, LSZH cables are manufactured using halogen-free materials such as cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) or ethylene propylene rubber (EPR). These cables are ideal for use in confined spaces, public buildings, and areas with stringent fire safety regulations.
Fire resistant cables are specifically engineered to maintain their functionality during a fire event. These cables are constructed using materials with high melting points and low thermal conductivity, such as mica tape or ceramic fibers, to withstand extreme heat and prevent electrical failure. Fire resistant cables are commonly used in critical applications such as emergency lighting systems, fire alarms, and evacuation systems.
Armored flame retardant cables are reinforced with a layer of metallic armor, typically made of steel or aluminum, to provide mechanical protection and enhance fire resistance. The armor acts as a barrier against physical damage and helps contain the spread of fire, making these cables suitable for harsh industrial environments, outdoor installations, and underground applications.
Flame retardant cables are classified based on their fire performance characteristics, as defined by international standards and regulations. The classification criteria typically include parameters such as flame propagation, smoke emission, and toxicity. Some common classification standards for flame retardant cables include:
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) standard 60332 defines test methods for assessing the flame propagation characteristics of cables. Cables are classified based on their ability to resist flame propagation when subjected to vertical or horizontal flame tests. Higher classification ratings indicate better flame retardant properties.
The British Standard BS 6387 specifies test procedures for evaluating the fire resistance of cables under various conditions, including fire, water, and mechanical shock. Cables are classified into different categories (e.g., CWZ, SWA, and CWZ) based on their performance during fire tests involving direct flame exposure, water spray, and mechanical impact.
Underwriters Laboratories (UL) standard 94 provides a classification system for assessing the flammability of plastic materials, including cable insulation and sheathing materials. Cables are classified into different flame rating categories (e.g., V-0, V-1, and V-2) based on their performance during vertical flame tests and combustion behavior.
Flame retardant cables find widespread applications across various industries and sectors where fire safety is a critical concern. Some common applications include:
In commercial and residential buildings, flame retardant cables are used for electrical wiring, lighting, and power distribution systems. These cables help mitigate the risk of fire hazards in occupied spaces, corridors, and stairwells, ensuring the safety of occupants and property.
Industrial facilities such as manufacturing plants, refineries, and chemical processing plants require robust fire protection measures to safeguard personnel and assets. Flame retardant cables are used in critical applications such as control systems, instrumentation, and motor connections, where fire resistance is essential for uninterrupted operation.
In transportation systems such as railways, airports, and tunnels, flame retardant cables are deployed to ensure the integrity of electrical and communication networks. These cables are designed to withstand the harsh operating conditions and potential fire hazards associated with confined spaces and high-temperature environments.
The oil and gas sector relies on flame retardant cables for offshore platforms, drilling rigs, and petrochemical facilities. These cables are engineered to withstand extreme weather conditions, corrosive environments, and the risk of hydrocarbon fires, ensuring the safety and reliability of critical infrastructure.
Data centers house mission-critical IT equipment and infrastructure, making fire safety a top priority. Flame retardant cables are used extensively in data center applications, including server racks, network cabinets, and power distribution units, to minimize the risk of fire-related downtime and data loss.
The difference between flame retardant cables and ordinary cables lies primarily in their ability to resist the propagation of fire and minimize the risks associated with fire hazards. Here are the key distinctions between the two:
Flame retardant cables are specifically engineered to inhibit the spread of fire along their length. They are constructed using materials that possess inherent fire-resistant properties or are treated with flame-retardant additives. In contrast, ordinary cables do not have the same level of fire resistance and may contribute to the spread of fire if ignited.
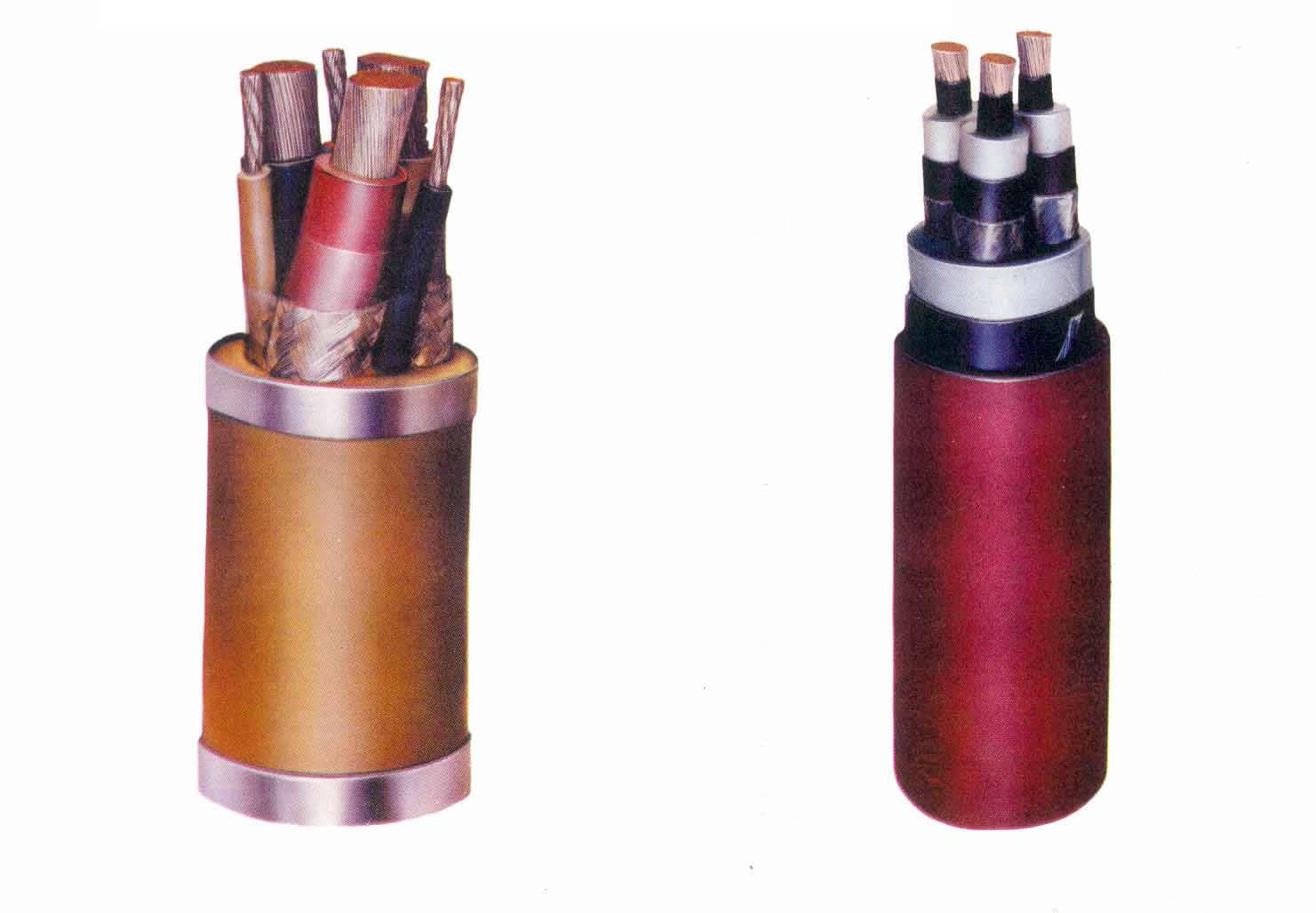

Flame retardant cables typically feature insulation and sheathing materials that are designed to withstand high temperatures and resist combustion. These materials may include halogen-free compounds, mica tape, or ceramic fibers, depending on the specific requirements of the application. Ordinary cables, on the other hand, may use standard insulation materials such as PVC or XLPE without additional flame-retardant properties.
Flame retardant cables are manufactured in compliance with stringent safety standards and regulations governing fire performance and flammability. These standards, such as IEC 60332, BS 6387, and UL 94, define test methods and classification criteria for assessing the fire resistance of cables. Ordinary cables may not meet the same rigorous standards and may pose a higher risk of fire hazard in certain environments.
Flame retardant cables are commonly used in applications where fire safety is a critical concern, such as commercial buildings, industrial facilities, transportation systems, and data centers. They are deployed in areas where there is a higher risk of fire ignition or where the consequences of a fire event could be catastrophic. Ordinary cables, on the other hand, may be suitable for non-critical applications where fire resistance is not a primary consideration.
Due to their specialized construction and enhanced fire resistance properties, flame retardant cables may be more expensive than ordinary cables. The additional materials and manufacturing processes required to achieve fire resistance can contribute to higher production costs. However, the investment in flame retardant cables is justified by the added safety benefits they provide in fire-prone environments.
Flame retardant cables play a crucial role in enhancing fire safety and mitigating the risks associated with electrical installations. From PVC insulated cables to LSZH cables and fire-resistant variants, these cables offer a diverse range of solutions to meet the stringent requirements of different industries and applications. By understanding the types, classification, and applications of flame retardant cables, engineers, designers, and facility managers can make informed decisions to protect lives, property, and critical infrastructure from the devastating effects of fire. As advancements in materials and technology continue to drive innovation in fire protection solutions, flame retardant cables will remain indispensable components in the arsenal of fire safety measures across the globe.