For the high-voltage cable, we can see the main pole on the wire, underground pipe network cable. High voltage cable selection considerations are quite complex, because it is rather a variety. The following is tantamount to understand the selection principles of high-voltage cables.
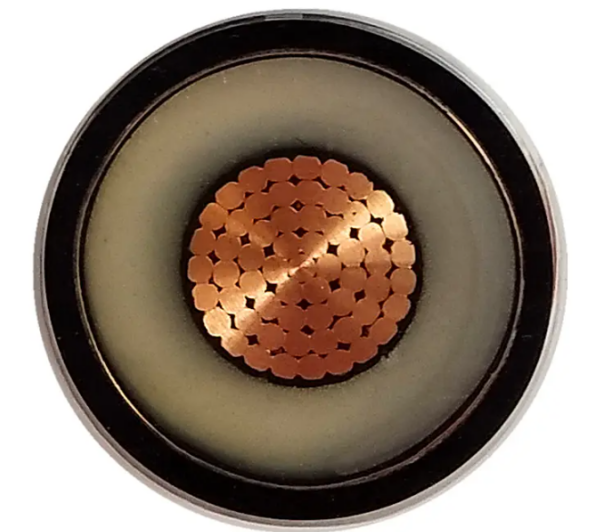

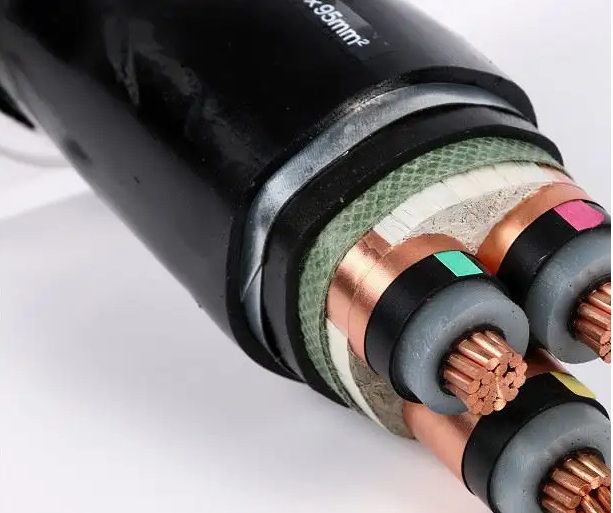
Components of high voltage cable from inside to outside include: conductor, insulation, inner sheath, filling material (armored), outer insulation. Of course, armored high-voltage cables are mainly used in the ground, can resist the superior strength of the ground pressure, and can prevent other external damage.
The principal types of high-voltage cables are YJV cable, VV cable, YJLV cable, and VLV cable.
YJV cable Full name Cross-linked polyethylene insulated PVC sheathed power cable (copper core).
VV cable full name PVC insulated PVC sheathed power cable (copper core).
YJLV cable full name cross-linked polyethylene insulated PVC sheathed aluminum core power cable.
VLV cable full name PVC insulated PVC sheathed aluminium core power cable.
1. Buried, refers to the high-voltage cables directly laid underground (buried depth varies according to different geological conditions, generally greater than 0.7 meters). The buried laying requires higher protection of cable itself, so it is suitable to use armored cable with an outer protective layer.
For some unstable geological conditions such as swamp and quicksand, wire armored cables can also be selected. Armored cable is characterized by stiff, internal materials and conductors are not the same, and the metal sleeve has an insulating layer.
2. Pipe type refers to lay high voltage cables in prefabricated pipes. This way of playing is easy to cause the cable overheating, resulting in power loss and capacity decline, so it is more suitable to use plastic protective sheath cable or bare armored cable.
3. Tunnel type refers to the laying of high-voltage cables on the bridge or support in the cable tunnel. This laying method is mostly used in the city, with the characteristics of good heat dissipation and easy maintenance, but the requirements for cable flame retardant are high, suitable for bare armored cable or flame retardant plastic sheath cable.
4. Overhead, refers to the high-voltage cable through the pole (pole) connection laying. This way of playing is suitable for flat terrain and less undulating area. However, this approach makes the cable completely exposed to the outer space, which is easy to be affected by the external environment and external forces. It is appropriate for cables with outer layers or plastic cables.
According to the cause of the fault is classified into the following categories: manufacturer manufacturing reasons, construction quality reasons, design unit design contributors, external force damage four categories.
According to different parts of the manufacturer, the manufacturing factors are divided into three categories: high-voltage cable body reasons, high-voltage cable joint reasons, and high-voltage cable grounding system reasons.
1. Cable body manufacturing reasons: Generally in the production process of high-voltage cable prone to problems are insulation eccentricity, insulation shielding thickness is uneven, insulation impurities, internal and external shielding protrusion, cross-linking degree is uneven, high-voltage cable damp, high-voltage cable metal sheath sealing poor.
In some serious cases, faults may occur in the completion test or shortly after being put into operation, and most of them exist in the form of defects in the cable system, causing serious hidden danger to the long-term safe operation of the cable.
2. Manufacturing reasons for high-voltage cable connectors: high-voltage cable connectors used to be wrapped type, mold casting type, molding type and other types, which require a large amount of work to be made on site, and because of the limitation of field conditions and production process. There will inevitably be air gaps and impurities between the insulating tape layers, so it is subject to problems.
The high-voltage cable connector is divided into cable terminal connector and cable middle connector. No matter what type of connector, the cable connector fault usually occurs at the cable insulation shield fracture.
Because this is the place where the electrical stress is concentrated, the reasons for the dual failure of the high voltage cable due to manufacturing reasons include manufacturing defects of the stress cone body, insulation filler problems, oil leakage of the seal ring and other reasons.
3. High voltage cable grounding system: high voltage cable grounding system includes cable grounding box, cable grounding protection box (with protective layer protector), cable cross interconnection box, protective layer protector and other parts.
Generally, the problem is mainly because the box seal is not good and the water inlet leads to multi-point grounding, which causes the induced current of the metal shielding layer to be too large. In addition, the parameter selection of the protective layer is not reasonable or the quality is not good. The instability of the zinc oxide crystal is also easy to cause the ruin of the protective layer.

There are countless cases of high-voltage cable system failure due to construction quality. The main reasons are as follows: First, the site conditions are poor, the environment and process requirements of high-voltage cables and joints are very high when manufactured in the factory, and the temperature, humidity and dust of the construction site are not easy to control.
Second, the construction process of high-voltage cable will inevitably leave small slip marks on the insulation surface, semi-conductive particles and sand particles on the emery cloth may also be embedded in the insulation, in addition, because the insulation is exposed to the air in the construction process of the joint, moisture will also be inhaled in the insulation, which leave hidden dangers for long-term safe operation.
Third, the high-voltage cable installation is not in strict accordance with the process construction or process regulations do not take into consideration the possible problems.
Four are the completion acceptance of DC voltage test caused by the formation of anti electric field in the joint leading to insulation damage.
Five are the high voltage cable due to poor sealing treatment. The intermediate joint must be sealed with a copper shell plus PE or PVC insulation and anti-corrosion layer, so as to ensure the compactness of lead seal in the field construction, which effectively ensures the sealing and waterproof performance of the joint.
The breakdown is caused by the extrusion of the high voltage cable owing to the thermal expansion. When the load of cross-linked cable is prohibitive, the core temperature will rise and the cable will be thermally expanded.
At the turning point in the tunnel, the cable top will be on the facade of the bracket, and the crawling force of the cable will be great during long-term heavy load operation. As a result, the facade of the bracket will break the outer sheath and the metal sheath of the cable, and the insulation layer of the high-voltage cable will be squeezed into the cable, leading to cable breakdown.
Well, that's all for today's introduction.